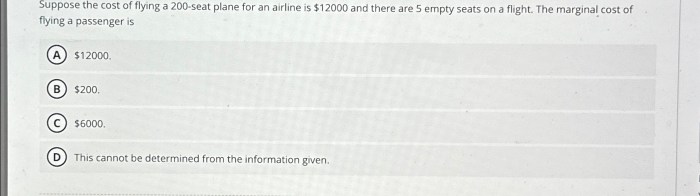
Suppose the cost of flying a 200 seat plane – Suppose the cost of flying a 200-seat plane sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with gaya akademik dengan tone otoritatif and brimming with originality from the outset.
This comprehensive analysis delves into the economic impact, operational considerations, market analysis, revenue generation, and cost optimization strategies associated with operating a 200-seat aircraft, providing valuable insights for industry professionals, researchers, and aviation enthusiasts alike.
Economic Impact
Flying a 200-seat plane involves significant economic considerations, including direct and indirect costs. Direct costs encompass fuel expenses, maintenance, and crew salaries. Indirect costs include airport fees, insurance, and marketing expenses.
Fixed costs, such as aircraft depreciation and insurance, remain relatively constant regardless of flight frequency. Variable costs, including fuel and crew expenses, fluctuate with flight activity.
Fuel prices play a major role in determining the cost of flying, as they account for a significant portion of operating expenses. Economic factors, such as inflation and currency fluctuations, can also impact the cost of operations.
Operational Considerations: Suppose The Cost Of Flying A 200 Seat Plane
Operational costs are another crucial aspect of flying a 200-seat plane. Maintenance expenses are essential for ensuring aircraft safety and reliability. Crew costs, including pilot and cabin crew salaries, represent a significant portion of operational expenses.
Aircraft utilization, measured as the number of flight hours per day, directly impacts costs. Higher utilization leads to lower costs per flight hour. Flight frequency also affects costs, as more frequent flights require additional crew and maintenance resources.
Market Analysis
Understanding market demand is vital for optimizing revenue generation. Air travel demand is influenced by factors such as economic conditions, travel preferences, and competitive pricing.
Airlines must analyze the competitive landscape and develop pricing strategies that attract customers while maximizing revenue. Target market identification and customer demographics are essential for tailoring marketing efforts and enhancing customer satisfaction.
Revenue Generation
Flying a 200-seat plane involves various revenue streams. Ticket sales generate the primary revenue, while ancillary fees, such as baggage charges and seat upgrades, provide additional income.
Pricing strategies significantly impact revenue generation. Airlines use revenue management systems to optimize ticket prices based on demand and competition. Ancillary fees can supplement revenue and enhance profitability.
Cost Optimization Strategies
Airlines employ cost optimization strategies to minimize expenses and improve profitability. Technology plays a vital role in optimizing maintenance and operational processes, reducing costs.
Operational efficiency measures, such as fuel-efficient flight operations and reduced aircraft turnaround times, contribute to cost savings. Airlines also explore partnerships and alliances to share resources and reduce expenses.
Successful cost-cutting initiatives have been implemented by airlines, such as the use of composite materials to reduce aircraft weight, leading to lower fuel consumption.
Answers to Common Questions
What are the primary factors that influence the cost of flying a 200-seat plane?
The cost of flying a 200-seat plane is influenced by a combination of fixed costs (such as aircraft acquisition, depreciation, and insurance) and variable costs (such as fuel, maintenance, and crew expenses). Economic factors, such as fuel prices and market conditions, can also significantly impact operating costs.
How does aircraft utilization affect the cost of flying a 200-seat plane?
Aircraft utilization, measured by the number of hours an aircraft is flown per day, has a direct impact on costs. Higher utilization typically leads to lower per-flight costs, as fixed costs are spread over a larger number of flights. However, it is important to balance utilization with maintenance requirements and crew availability.
What are some key revenue streams for airlines operating 200-seat planes?
Airlines generate revenue through a combination of ticket sales, ancillary fees (such as baggage fees and seat selection charges), and other sources such as cargo and loyalty programs. Optimizing revenue generation involves understanding market demand, competitive pricing strategies, and customer demographics.
How can airlines optimize costs for flying a 200-seat plane?
Cost optimization strategies include leveraging technology to improve operational efficiency, implementing fuel-saving measures, optimizing crew scheduling, and negotiating favorable contracts with suppliers. Data analytics and continuous improvement initiatives are essential for identifying and implementing cost-effective solutions.