Select the correct statement describing sympatric speciation – Sympatric speciation, the process of new species evolving from an existing species without geographical isolation, has captivated evolutionary biologists for decades. This intriguing phenomenon challenges traditional views of speciation and offers insights into the remarkable diversity of life on Earth.
Sympatric speciation occurs when two populations of the same species evolve reproductive isolation while living in the same geographic area. This isolation can result from various mechanisms, including natural selection and genetic drift. Once reproductive isolation is established, the two populations can no longer interbreed, leading to the formation of distinct species.
1. Define Sympatric Speciation
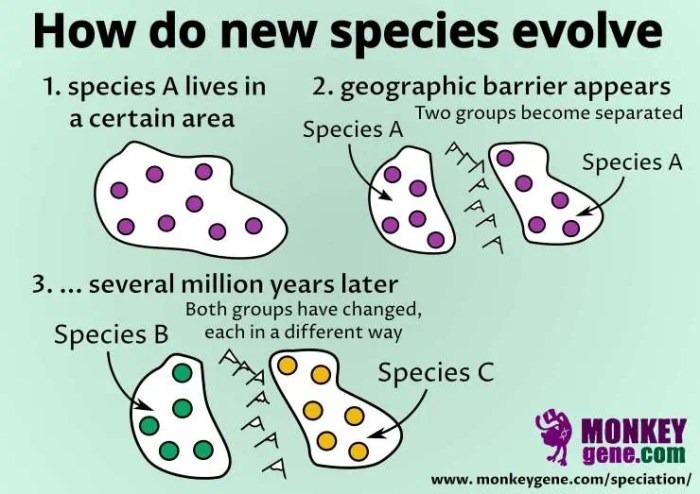
Sympatric speciation is the formation of two or more new species from a single ancestral species within the same geographic area. It is distinct from allopatric speciation, which occurs when a population is divided into two or more geographically isolated groups.
Sympatric speciation is a relatively rare phenomenon, but it has been documented in a variety of organisms, including plants, animals, and insects.
Examples of Sympatric Speciation
- Apple maggot fly (Rhagoletis pomonella): This species of fly has diverged into two distinct populations that feed on different host plants. One population feeds on apples, while the other population feeds on hawthorns.
- Lake Victoria cichlids: This group of fish has undergone a remarkable radiation of sympatric speciation, resulting in the formation of over 500 distinct species.
2. Mechanisms of Sympatric Speciation
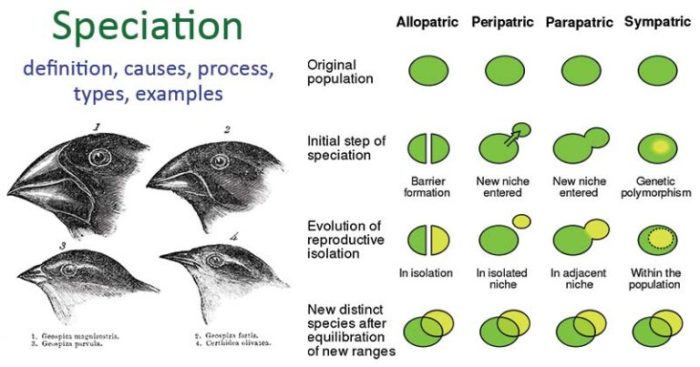
The mechanisms of sympatric speciation are not fully understood, but several factors are thought to play a role.
Natural Selection
Natural selection can favor the evolution of reproductive isolation between two populations that live in the same area. For example, if two populations of the same species feed on different resources, natural selection may favor the evolution of different beak shapes in each population.
Reproductive Isolation, Select the correct statement describing sympatric speciation
Reproductive isolation is essential for sympatric speciation to occur. Without reproductive isolation, the two populations would simply interbreed and merge back into a single population.
There are a number of different mechanisms that can lead to reproductive isolation, including:
- Prezygotic isolation: This type of isolation prevents the formation of zygotes between two populations. Examples of prezygotic isolation include differences in mating behavior, habitat preferences, and gamete incompatibility.
- Postzygotic isolation: This type of isolation prevents the development of viable offspring from zygotes that are formed between two populations. Examples of postzygotic isolation include hybrid inviability and hybrid sterility.
3. Examples of Sympatric Speciation
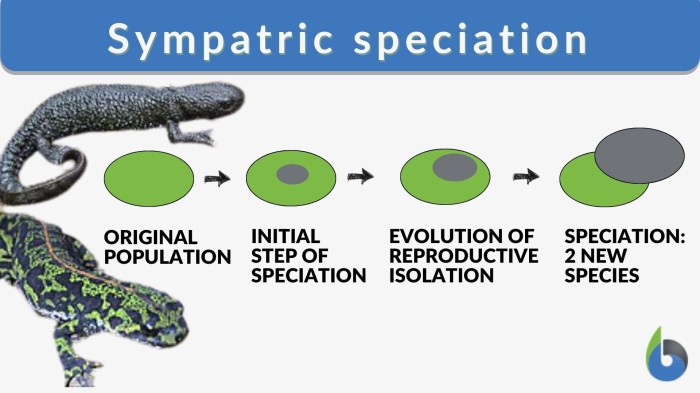
Sympatric speciation has been documented in a variety of organisms, including plants, animals, and insects.
Case Studies
- Apple maggot fly (Rhagoletis pomonella): This species of fly has diverged into two distinct populations that feed on different host plants. One population feeds on apples, while the other population feeds on hawthorns. The two populations are reproductively isolated due to differences in their mating behavior and host plant preferences.
- Lake Victoria cichlids: This group of fish has undergone a remarkable radiation of sympatric speciation, resulting in the formation of over 500 distinct species. The cichlids have diverged into different species due to a combination of natural selection and reproductive isolation.
Evidence
There is a growing body of evidence to support the occurrence of sympatric speciation. This evidence includes:
- The presence of closely related species that live in the same geographic area.
- The existence of reproductive isolation between these species.
- The presence of genetic evidence that supports the hypothesis of sympatric speciation.
4. Evolutionary Significance of Sympatric Speciation: Select The Correct Statement Describing Sympatric Speciation
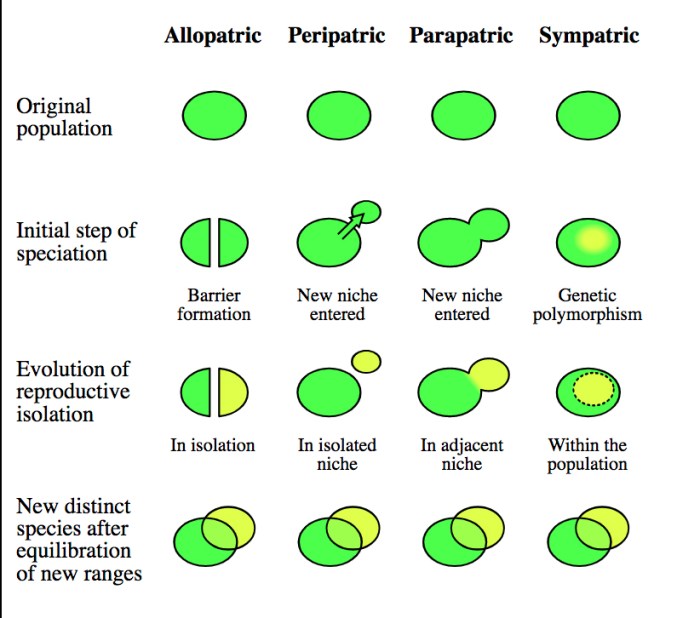
Sympatric speciation is a significant evolutionary phenomenon because it can lead to the formation of new species without the need for geographic isolation.
Sympatric speciation has played a major role in the evolution of biodiversity. For example, it is thought to be responsible for the evolution of the apple maggot fly and the Lake Victoria cichlids.
Sympatric speciation also has implications for understanding evolutionary processes. For example, it suggests that natural selection can play a major role in the evolution of reproductive isolation.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the key difference between sympatric and allopatric speciation?
Sympatric speciation occurs when new species evolve without geographical isolation, while allopatric speciation occurs when new species evolve in geographically isolated populations.
Can sympatric speciation occur rapidly?
Yes, sympatric speciation can occur relatively quickly, especially in organisms with short generation times and high mutation rates.
What are some examples of sympatric speciation?
Examples include the evolution of apple maggot flies from hawthorn flies and the divergence of cichlid fish species in Lake Victoria.